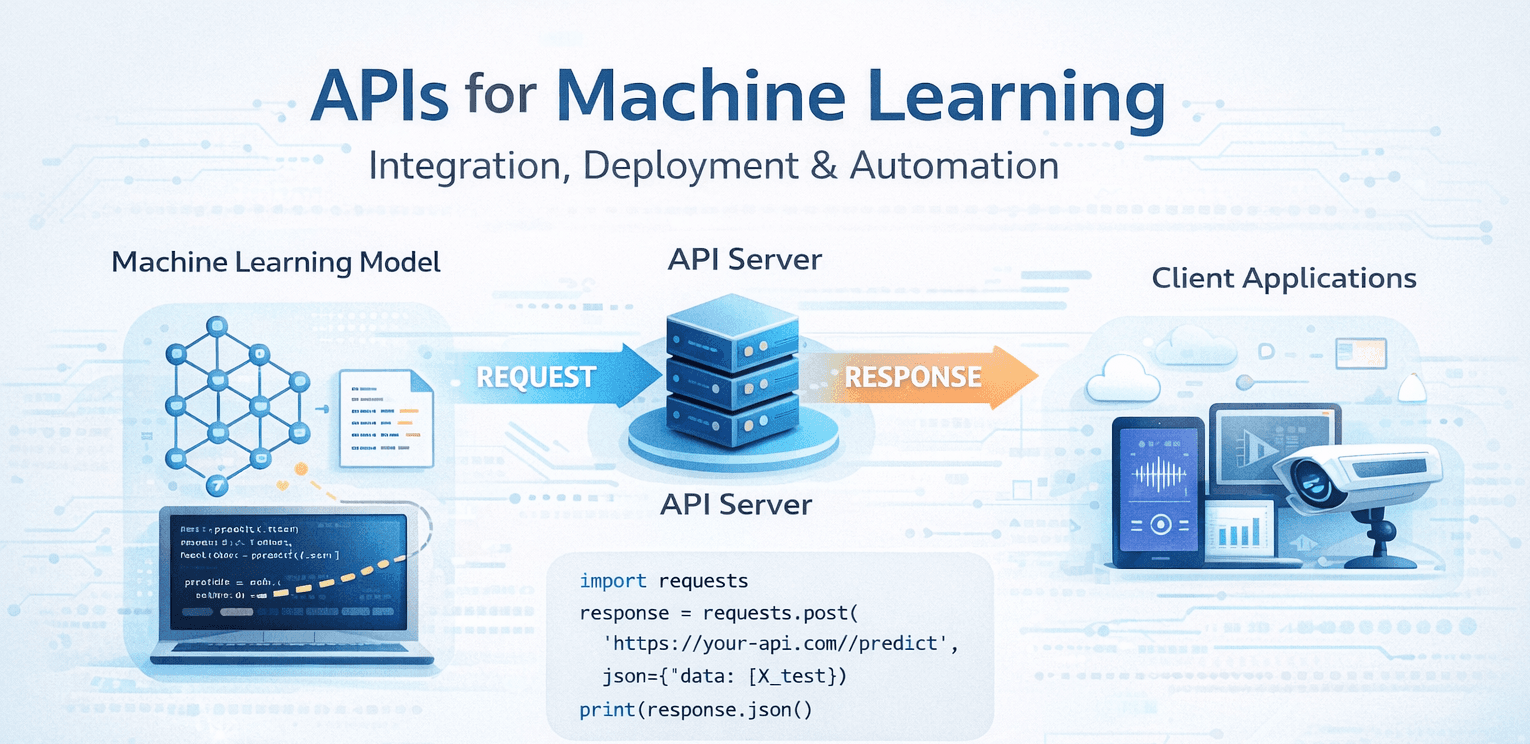
Connecting Models to the Real World
Training a machine learning model is only half the job.
The real challenge begins when you want to use that model in an application — a website, mobile app, or another system.
That’s where APIs for Machine Learning come in.
This article explains:
What ML APIs are
Why they matter
How they work
A simple example using Python
How ML models are deployed using APIs
No heavy theory — just practical understanding.

🧠 What Are APIs for Machine Learning?
An API for Machine Learning is a bridge that allows other applications to send data to a trained ML model and receive predictions.
In simple words:
An ML API lets your model talk to the outside world.
Instead of running ML code inside a notebook, you expose it as an endpoint that anyone (or any system) can call.
🔁 How ML APIs Work (High-Level Flow)


Step-by-step flow:
A client (web app, mobile app, script) sends data
The API server receives the request
The ML model processes the input
The prediction is returned as a response (usually JSON)
This turns your ML model into a service, not just code.
📦 Why APIs Are Essential in Machine Learning
Without APIs:
Models stay stuck in notebooks
No real-world usage
No scalability
With APIs, you can:
🚀 Deploy models to production
🌐 Connect frontend and backend
🤖 Automate predictions
🔄 Update models without changing apps
Modern AI systems are API-first by design.
🧩 Common Use Cases of ML APIs

ML APIs are widely used for:
Image classification
Face recognition
Spam detection
Recommendation systems
Medical diagnosis
Fraud detection
Examples:
POST /predict-image
POST /sentiment
POST /detect-fraud
🛠️ Building a Simple ML API (Concept)
Let’s imagine you already trained a model.
Now you want:
“Send input → get prediction”
Minimal API Structure
Client → API → ML Model → Prediction → Client
🧪 Example: ML Prediction API Using FastAPI
Below is a very simple example of exposing an ML model as an API.
Step 1: Create the API
from fastapi import FastAPI
import joblib
app = FastAPI()
model = joblib.load("model.pkl")
@app.post("/predict")
def predict(data: list):
prediction = model.predict([data])
return {"prediction": int(prediction[0])}
📌 What this does:
Loads a trained model
Accepts input data
Returns predictions as JSON
Step 2: Call the API (Client Side)
import requests
url = "<http://127.0.0.1:8000/predict>"
data = {"data": [5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2]}
response = requests.post(url, json=data)
print(response.json())
This is how ML becomes usable software.
📄 Why JSON Is Used in ML APIs
JSON is preferred because it is:
Lightweight
Human-readable
Language-independent
Typical ML API response:
{
"prediction": "cat",
"confidence": 0.92
}

🔐 Security & Best Practices
ML APIs must be protected.
Best practices:
Use authentication (API keys / tokens)
Validate inputs
Limit request size
Handle errors properly
Monitor performance
Never expose:
Model files
Training data
API keys in code
🌍 ML APIs in Real-World Systems

Typical production setup:
Frontend → API Gateway
API → ML Model
Logs → Monitoring system
Storage → Model versions
This is how AI moves from research to reality.
🧠 Key Takeaways
If you remember only three things:
✔️ ML models are useless without deployment
✔️ APIs make ML models accessible
✔️ APIs turn AI into real products
Once you understand ML APIs, you unlock:
AI applications
SaaS platforms
Scalable ML systems
📚 References
MDN Web Docs
What is an API?
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/JavaScript/Client-side_web_APIs/Introduction
FastAPI
FastAPI Documentation
TensorFlow
TensorFlow Serving
IBM
What are ML APIs?
Towards Data Science
Deploying Machine Learning Models as APIs
Wikipedia
Machine Learning